With the demand for portable electronics ever increasing, the need to produce more compact devices with ever-increasing capabilities calls for engineering solutions that combine functionality with flexibility. In this blog, we introduce some representative rigid-flex board constructions in flexible PCB manufacturing experience.
Rigid-Flex boards can be shaped to fit where no other design solution can. They are an integrated hybrid of printed circuit board and flex board PCB technology and exhibit the benefits of each. This allows substantially greater freedom of packaging geometry and a significant reduction of interconnects while retaining the precision, density and repeatability of printed circuit board technology.
Table of Contents
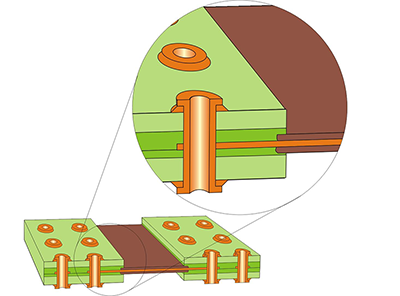
Traditional Rigid-Flex Board Construction: Coverlay extends over all internal circuitry
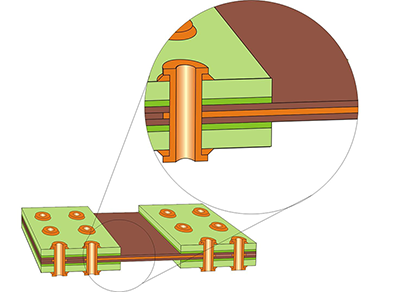
Short Coverlay Rigid-Flex Board Construction: Coverlay does not extend over Internal circuits
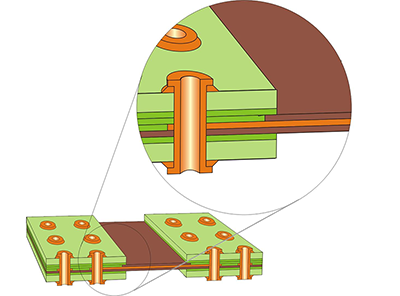
Hybrid Laminate Rigid-Flex Board Construction: Copper foil covers lapped rigid and flex PCB materials
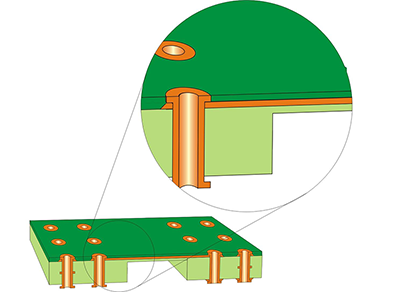
Surface Flex Rigid-Flex Board Construction: Flex circuit on outer surfaces only
All Rigid Material Rigid-Flex Board Construction: Rigid laminate material routed to thickness that will bend using suitable radius. Flexible coverlay normally needed
Reinforced Flex PCB Construction: Flex circuit bonded to rigid stiffener
The Basic Process
Double-sided flex PCB is built with coverlay but no holes
Rigid caps are scored for later removal and laminated to flex using bondply or pre-preg
Circuit is drilled and processed like standard multilayer circuit. After routing the scored areas are removed to allow circuit to flex
Applications of Rigid-Flex boards can be found throughout the electronics industry and in the most demanding applications including industrial control, medical and military.
Rigid-Flex PCB design has evolved significantly over the past decade. Modern designs require the rigid areas to be fully capable “rigid” boards. The same limits of complexity and density are pushed as in modern PCB’s including: fine lines/spacing, high aspect ratio vias, blind and buried vias, high layer counts, higher operating temperatures, and RoHS assembly compliance.
As a PCB manufacturer, MAD PCB manufactures single-, double-, and multi-layered flexible printed circuits using modern rigid-flex materials and construction. Designs comply with IPC-2223 standards, which define the elimination/minimization of adhesive use within rigid areas, use of adhesiveless FCCL, and use of selective or partial coverlay construction.
In Gerber reviewing and quote stage, rigid-flex board’ specifications, materials, and construction are carefully examined in order to minimize and eliminate any technical issues. Areas of opportunity for improved reliability, functionality, and cost reductions are also identified to generate an accurate quote that is based on a manufacturable, reliable and cost-effective design.