Table of Contents
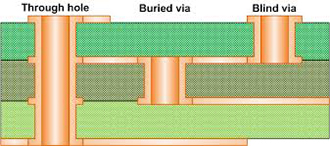
Blind and Buried Vias
Due to the increasing complexity of printed circuit board structures, blind vias and buried vias (or blind microvias) are increasingly used in multilayer HDI boards.
What’s Blind and Buried Vias, Blind Vias and Buried Vias?
As per IPC-A-600G, the definitions of them are as below:
- Blind and Buried Vias: Plated-through holes connecting two or more conductive layers of multilayer printed board, but not extending fully all layers of the base material comprising the board, are called blind and buried vias.
- Blind Vias: Blind via plated-through holes extend from the surface and connect the surface layer with one or more internal layers. The blind via can be produced by two methods:
- After multilayer lamination by drilling a hole from the surface to the internal layers desired and electrically interconnecting them by plating the blind via holes during the plating process.
- Before multilayer lamination by drilling the blind via holes from the surface layers to the first or last buried layers and plating them through, imaging and etching the internal sides, and then laminate them in the multilayer bonding process.
For the 2nd process, if an interconnection is desired between the surface layer and more than one internal layer, sequential etching, laminating, drilling and plating-through of these layers together before final multilayer lamination is required. Blind via holes should be filled or plugged with a polymer or solder resist to prevent solder form entering them as solder in the small holes decreases reliability.
- Buried Vias: Buried via plated-through holes do not extend to the surface but interconnect only internal layers. Most commonly the interconnection is between two adjacent internal layers. These are produced by drilling the thin laminate material, plating the holes through and then etching the internal layer pattern on the layers prior to multilayer lamination. Buried vias between non-adjacent layers requires sequential etching of inside layers, laminating them together, drilling the laminated panel, plating the holes through, etching external sides and laminating this panel into the final multilayer panel.
Blind and buried vias are used to connect between layers of a printed circuit board where space is at a premium. But not all combinations are possible. It is specified by UL that three thermal press cycles are the maximum. Thus, for maximum reliability and quality we cannot produce multi-layer PCB boards that require more than 3 lamination steps. What this means is you may bot design vias in such a way that it would take more than 3 steps to assemble them. Besides, blind and buried vias add considerably to the cost of a circuit board. They should only be used when absolutely necessary. To help PCB designers of tight printed boards, we offer via holes down to 0.2mm, and microvia down to 0.1mm(4mil). These need minimum outer layer pad sizes of 0.45mm and 0.4mm respectively.
Hole Size of Blind and Buried Vias
Small holes are usually used for either blind or buried vias and may be produced mechanically, by laser or by plasma techniques. The minimum drilled hole size for buried vias is shown in Table-1 and the minimum drilled hole size for blind vias is shown in Table-2, In either case plating aspect ratios must be considered; small deep blind vias are very difficult to plate because of decreased throwing-power and limited plating solution exchange in the holes. Blind and buried via holes may be plated shut; thus, the master drawing call out should be similar to that used for through-hole vias. See sectional standards for more information.
Table-1 Minimum Drilled Hole Size for Buried Vias
| Layer Thickness | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
| <0.25mm | 0.10mm | 0.10mm | 0.15mm |
| 0.25-0.5mm | 0.15mm | 0.15mm | 0.20mm |
| 0.5mm | 0.15mm | 0.20mm | 0.25mm |
Table-2 Minimum Drilled Hole Size for Blind Vias
| Layer Thickness | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
| <0.1mm | 0.10mm | 0.10mm | 0.20mm |
| 0.10-0.25mm | 0.15mm | 0.20mm | 0.30mm |
| 0.25mm | 0.20mm | 0.30mm | 0.40mm |
IPC-6012 Surface and Hole Copper Plating Requirements
When the PCB layer count is more than 2 layers, the surface and hole copper plating requirements as Table-3 for plated through holes, blind vias and buried vias (not applicable for microvias). Copper plating thickness shall be continuous and wrap from hole walls onto outer surface. Refer to IPC-A-600 for discussion on copper plating thickness for hole walls.
| IPC-6012 | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
| Copper -average | 20μm [787μin] | 20μm [787μin] | 25μm [984μin] |
| Minimum thin areas | 18μm [709μin] | 18μm [709μin] | 20μm [787μin] |
| Minimum Wrap | AABUS | 5μm [197μin] | 12μm [472μin] |
Via plating is the process of filling a drilled hole with copper to provide a path for current from a surface of the board to an inner layer, between two inner layers or from one surface to the other.
Blind and Buried Vias Design
- For PCB cost reasons, we recommend avoiding an overlap of blind and buried vias in the layer build-up. For example, avoid blind vias from L1-L3 and simultaneously buried vias from L2-L4.
- Blind and Buried via holes for each connection level must be defined as separate drill files.
- The ratio of blind via’s drill diameter to hole depth (aspect ratio) must be 1:1 or larger, and that of buried vias must be 1:12 or larger.
- Blind vias can be placed within pads (via in pad).
- The larger you choose the annular rings on inner layers, the more stable the connection and via reliability.
Manufacturing Capabilities
We use combination of depth-controlled laser drilling and mechanical NC drilling to manufacture the blind and/or buried vias. The manufacturing capabilities for standard PCBs and HDI PCBs as following Table-4.
| Blind or Buried Via | Aspect Ratio | Ø min | Ø max | Via Pad | Annular Ring |
| Blind Via (mechanical) | 1:1 | 200μm | 300μm | 400μm | 100μm |
| Special Blind Fabrication | 1:1.2 | 150μm | 150μm | 350μm | 100μm |
| Blind Via (Laser) | 1:1 | 100μm | 100μm | 280μm | 90μm |
| Buried Via (mechanical) | 1:10 | 200μm | 400μm | 400μm | 100μm |
| Special Buried Fabrication | 1:12 | 150μm | 400μm | 330μm | 90μm |
Click to check our advanced PCB Fabrication Process and PCB Capabilities
Advantages of Blind and Buried Vias
- Increasing wiring layout density and saving PCB space.
- Reduction of layer count by widening the BGA breakout channel with a blind via.
- Elimination of electrical layers by replacing through-hole vias with microvias
- Reduction of PCB aspect ratio (PCB thickness /Drilled Hole Diameter)