What is an Operational Amplifier?
An Operational Amplifier (often Op amp, or opamp) is an integrated circuit (IC) that can amplify weak electric signals. An op amp has two input pins and one output pin. Its basic role is to amplify and output the voltage difference between the two input pins.
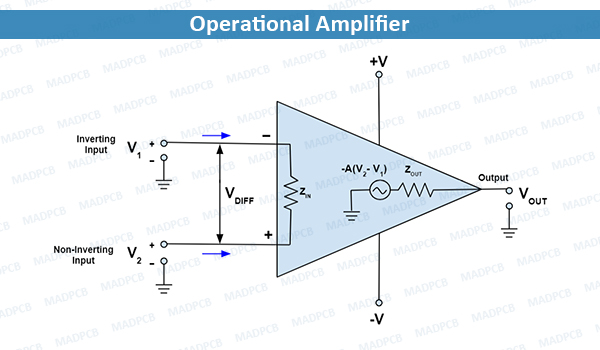
Operational Amplifier
An opamp is not used alone but is designed to be connected to other circuit to perform a great variety of operations. Here are some typical examples of usage of circuits with these amplifiers.
- Enables substantial amplification of an input signal: when an op-amp is combined with an amplification circuit, it can amplify weak signals to strong signals. It behaves like a megaphone where the input signal is a person’s voice and the megaphone is the operational amplifier circuit. For example, such a circuit can be used to amplify minute sensor signals. Processing of sensor signals can be further improved by inputting the amplified signal to a microcontroller unit (MCU).
- Enables elimination of noise from an input signal: By operating as a filter of input signals, the op-amp circuit is able to extract the signal with the target frequency. For example, when an operational amplifier circuit is used for voice recognition or in a voice recorder, it can extract frequencies close to the targeted sound while shutting out all other frequencies as noise. An operational amplifier circuit can be tweaked to perform a broad range of functions such as arithmetical operations or signal synthesis.
Applications of Operational Amplifier
A linear amplifier like an op amp has many different applications. It has a high open loop gain, high input impedance and low output impedance. It has high common mode rejection ratio. Due to these favorable characteristics, it is used for different application. In this article, we are discussing some of the most prominent uses of an Op amp. This is not an exhaustive list but covers the important applications of op amp within the scope of our discussion.
- Inverting Amplifiers
- Non-Inverting Amplifiers
- Phase Shifter
- Scale Changer
- Adder or Summing Amplifier
- Differential Amplifier
- Differentiator
- Integrator
- Voltage to Current Converter
- Current to Voltage Converter
- Logarithmic Amplifier
- Half Wave Rectifier
- Peak Detector
- Voltage Comparator
