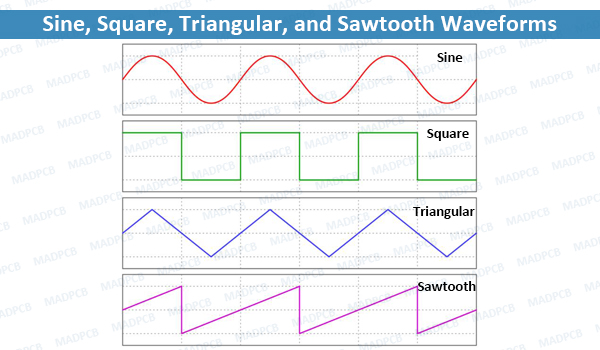
What’s Triangular Wave?
A Triangular Wave or Triangle Wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function.
Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse).
A triangle wave has a symmetrical rise and fall of the waveform, but a sawtooth (also called a ramp oscillator) rises very sharply (ideally instantaneously) and then falls gradually.
Triangle waves contain an infinite number of odd harmonics, which are often used in synthesizing musical sounds. They sound like horns and trombones. They are sometimes used in switch-mode power supplies and motor control circuits. They are often used as time-base or sweep generators and in subtractive audio synthesis as the harmonics are integers and easy to work with digitally.
Sawtooth waves contain an equal amount of even and odd harmonics (unlike square waves which contain only even harmonics that’s why the sound is more musical such as guitar and fuzz box).
One of the easiest ways to generate a triangle wave is from a relaxation oscillator generating a square wave and then integrating it.