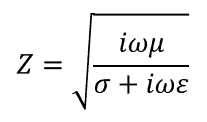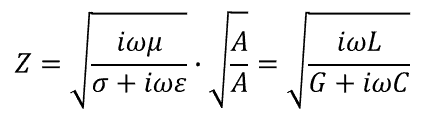What’s Wave Impedance?
Wave Impedance defines the impedance experienced by an electromagnetic waves as it travels through free space (i.e., vacuum) or some other medium. The impedance seen by propagating waves is the reason the magnetic field is so much weaker than the electric field, including the impedance of a vacuum.
- Every trace on a PCB has some impedance that defines how signals propagate through an interconnect.
- The impedance of a PCB trace is the impedance of the equivalent waveguide formed by the trace.
- The wave impedance is a general relation that can be extracted from your PCB interconnects and field solvers to better understand power transfer, radiation from a real PCB, and impedance matching.
Relationship to Transmission Line Impedance
This definition is the basis for deriving analytical expressions for waveguide impedance in various geometries, particularly in transmission lines. In general, for waves traveling in a dielectric with dispersion and losses, we have the following definition for wave impedance in terms of material constants for the dielectric:
This equation is applicable for any interconnect, waveguide structure, or unbounded dielectric. We can also use this to get back to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line. If we multiply the numerator and denominator by a cross-sectional area that bounds the electromagnetic field, we get back to the equation for transmission line impedance from circuit theory:
This nicely demonstrates the correspondence between waves impedance and transmission line/interconnect impedance -they really are the same. This correspondence between wave impedance and transmission line impedance is used to derive analytical expressions for transmission lines.
Deriving Transmission Line Impedance from Wave Impedance
If you want to get an analytical expression for transmission line impedance, such as the popular and highly accurate impedance equation, you need to derive the wave impedance for the transmission line structure. For some transmission lines, like a rectangular waveguide, this is very simple and is often given as a homework problem. For more complex structures, a more sophisticated method is used.