What’s a Plastic Film Capacitor?
A Plastic Film Capacitor is a capacitor that uses plastic film as the dielectric and aluminum or zinc as the electrodes to store electric charge.
What are Film Capacitors?
Film capacitors can be broadly categorized into plastic film capacitors, metallized plastic film capacitors, and composite film capacitors. The same dielectric materials are used in the construction of these different types of film capacitors. In composite film capacitors, a combination of dielectric materials is used in the construction of the component.
Film capacitors have characteristics that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of applications including filtering, decoupling, bypassing, EMI suppression, pulse coupling, blocking, and smoothing. Plastic film capacitors deliver high reliability under extreme environmental conditions. Compared to other capacitor types, plastic film devices have lower equivalent series resistance and dissipation factor.
In film capacitors, plastic film is used to construct the dielectric, and aluminum or zinc is used to construct the electrodes of the capacitor. Film capacitors are also known as plastic film capacitors or film dielectric capacitors. Plastic film capacitors are mainly used in circuits where low loss and high insulation resistance is required.
Brief History of Film Capacitors
Before film capacitors came in to application, paper capacitors were used in the decoupling circuits. Paper capacitors used impregnated paper which was placed with metal strips and rolled into cylindrical shapes. However, since these capacitors had paper as a dielectric, they were not only likely to be prone to environmental defects and were quite bulky in size. Therefore, scientists began searching for a solution that would minimize these problems.
It was the time when the plastic industry was booming and scientists discovered how the use of particular plastic films as dielectric offered long term stability in terms of its electrical parameters. It also helped in reducing the size, as multilayers of papers were replaced by just a few sheets of plastic. As the technology advanced, the size of these capacitors was reduced as thinner plastics with high reliability.
What are Dielectrics in Film Capacitors?
Dielectric is the insulating material placed between the electrodes of a capacitor. Plastic film capacitors offer high stability, long shelf life, low equivalent series resistance, low self-inductance, and a high ability to absorb power surges. The dielectric material used in a film capacitor greatly determines the properties of a component. Some of the key properties of a dielectric material that determine the performance of a capacitor include dielectric constant, dissipation factor, volume resistivity, maximum application temperature, dielectric strength, and dielectric absorption. These parameters vary from one dielectric material to another.
The most common dielectric materials used in the construction of plastic film capacitors are polypropylene and polyester. Other dielectrics used in the construction of film capacitors include polycarbonate, polystyrene, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), polyphenylene sulphide (PPS), polyimide, and paper.
- Polyester: Polyester has a high dielectric constant compared to polypropylene, and is one of the most widely used dielectric materials. This high dielectric constant allows construction of capacitors with small physical sizes. Polyester capacitors, also known as mylar capacitors, have good self-healing properties and are relatively cheap. At high temperatures, polyester capacitors dissipate more power. This characteristic makes these capacitors unsuitable for high frequency and high current AC applications. Furthermore, polyester exhibits a significant capacitance change, up to 5%, as temperature approaches low or high-temperature limits. Due to this characteristic, polyester is an unsuitable material for constructing precision capacitors. Polyester capacitors are mostly used in general purpose board level applications such as blocking, bypassing, decoupling, and some noise suppression circuits.
- Polypropylene: Polypropylene is commonly used in the construction of capacitors for high frequency AC applications. This dielectric material has a low dissipation factor, high breakdown strength, low dielectric absorption, high insulation resistance, and is readily available. These properties make polypropylene a dielectric material of choice for a wide range of applications including snubber circuits, high frequency AC systems, high voltage DC & AC systems, and high current DC applications. Polypropylene capacitors can operate over a wide temperature range. Unlike polyester capacitors, the capacitance of a polypropylene capacitor decreases with temperature. Due to its temperature characteristics, polypropylene capacitors are commonly used to complement polyester capacitors. This is achieved by connecting a polyester capacitor and a polypropylene capacitor in parallel. Despite its impressive properties, polypropylene has a lower dielectric constant than polyester. In addition, this material is not available in thin-gauge films. Compared to polyester, polypropylene is more expensive and is not a suitable material when physical size of a component is a key consideration.
- Polyphenylene sulphide (PPS): Polyphenylene sulphide has excellent temperature characteristics and is commonly used for constructing precision capacitors. The capacitance of these capacitors does not vary significantly with changes in temperature. PPS capacitors are commonly used to replace polycarbonate capacitors in electronic circuits. The dielectric constants of these two materials are similar, and both have high breakdown strength.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): PTFE capacitors, also known as Teflon capacitors, are low loss capacitors that offer excellent stability. PTFE has a relatively low dielectric constant, around 2.1, and it is, therefore, unsuitable for constructing components with small footprints. Teflon capacitors are suitable for high temperature applications and can be used in systems that expose components to temperatures of up to 200°C. PTFE capacitors have low capacitance values and are relatively expensive. Same materials in PTFE Rogers PCB.
- Polystyrene: Polystyrene capacitors exhibit extremely low loss and high capacitance stability over temperature, typically down to ±1% 0ver the range -55°C to +85°C. It’s low dielectric constant of 2.1 makes in suitable for low capacitance, high stability applications such as timing circuits.
- Polyimide (Kapton): Polyimide has a high dielectric constant, around 3.4, and it is commonly used for constructing components for high temperature applications. Kapton capacitors can be used in systems that can expose components to temperatures of up to 250°C. Metallized polyimide capacitors have poor self-healing characteristics.
- Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate has an average dielectric constant, around 2.7, and it is commonly used in the construction of capacitors for high temperature applications. Polycarbonate capacitors are low loss components that have good electrical characteristics over a wide temperature range. Polycarbonate capacitors were widely used in military applications. However, polycarbonate film has limited availability, and is not recommended for new designs.
The table below summarizes some characteristics of common plastic film dielectrics.
| Dielectric Material |
Dielectric Constant (Dk) |
Voltage Breakdown (V/ml) |
Dissipation Factor (%) |
Max. Operating Temperature (°C) |
| Polyester | 3.3 | 14,500 | <1.5 | 125 |
| Polypropylene | 2.2 | 16,250 | <0.1 | 105 |
| Polyethylene-napthalate (PEN) | 3.2 | 14,000 | <1 | 125 |
| Polyphenylene-sulfide (PPS) | 3 | 14,000 | <0.2 | 200 |
| Teflon (PTFE) | 2.1 | 7,000 | <1 | 200 |
Types of Plastic Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are classified into two types:
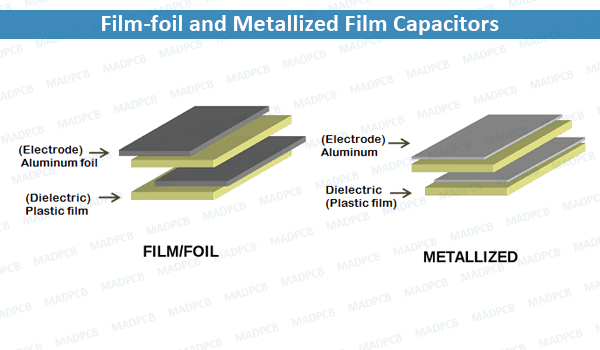
Film-foil and Metallized Film Capacitors
- Film-foil capacitors: The film-foil capacitor is made of two plastic films or sheets; each is layered with thin aluminum metal foil or sheet. The plastic sheets and aluminum sheets are then rolled in the form of a cylinder and wire leads are attached to the both ends of aluminum sheets. Polyester, polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate, and polyphenylene sulfide are commonly used as dielectric in film capacitors. In plastic film capacitors, aluminum sheets act as electrodes and plastic sheets acts as dielectric.
- Metallized film capacitors: In metallized film capacitors, the aluminum sheet or foil is replaced by a layer of metal vacuum deposited on the film layer. The most commonly used metal layer is aluminum or zinc that is extremely thin.
The plastic film layers made of synthetic material act as dielectric and the aluminum layers act as electrodes. The major advantage of film dielectric capacitors over natural dielectric capacitors is that the plastic film is synthetic or artificial. Therefore, we can able to increase thickness and heat resistance of the dielectric. In other words, we can change the thickness and heat resistance of the plastic film capacitor.
Applications of Film Capacitors
The various applications of film capacitors include:
- A/D converters
- Filters
- Motor run
- Peak voltage detectors
Advantages of Film Capacitors
- High stability
- Low cost
- Low losses even at high frequencies
