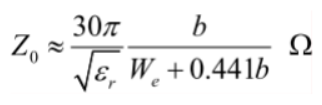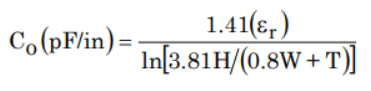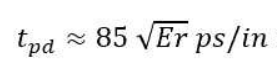What Is A PCB Stripline?
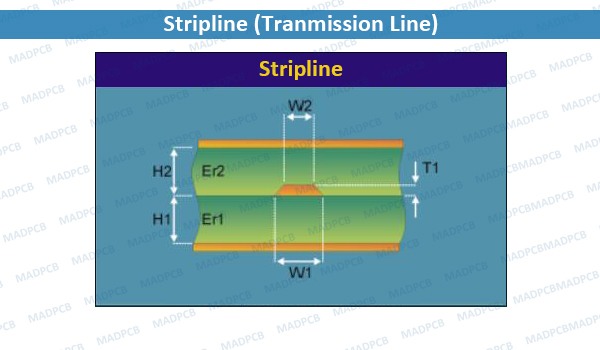
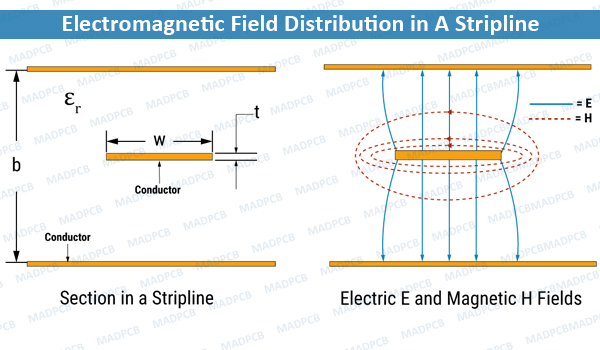
PCB Stripline is a transmission line, which is routed in inner layers of a printed circuit board (PCB), and that’s why it is surrounded by only one environment, i.e., PCB material. This technique is preferably used in a multilayer PCB design, and the signal trace is backed by the ground planes above and below.
In striplines, the current return path for a high-frequency signal trace is provided above and below the signal trace on the ground (power) planes. Due to this arrangement, the high-frequency signal remains inside the PCB leading to fewer emissions and also provides shielding against incoming spurious signals.
Characteristics Impedance of Striplines
The characteristic impedance of the stripline depends on the dielectric constant and on the cross-sectional geometry of the strip center-conductor and ground planes. The characteristic impedance decreases as the strip width We increases.
Note: b is the spacing between two planes and We is the effective strip width.
Characteristic Capacitance
Delay Constant
The propagation delay (Tpd) for a given length is only a function of the dielectric constant.
Stripline Design Considerations
Advantages of A Stripline Arrangement
- It provides shielding and protection to the signal traces.
- Low impedance, hence fewer emissions, and crosstalk
- Improvement can be seen above 50MHz
Stripline Arrangement Has Better EMI Characteristics
- Limitations of a signal trace arrangement
- It contains embedded signal traces, it is tough to debug such traces. In other words, PCB prototyping and troubleshooting would be difficult.
- Difficulty in decoupling
- Low impedance for proper matching
What Are the Losses in A Stripline?
- Finite conductivity of its conductors
- Magnetic resonances
- Finite resistivity and dumping phenomenon of the dielectric
Multi-layer Board Design with Stripline Geometry
Stripline is often required for multilayer circuit boards because it can be routed between the layers but grounding the transmission line requires due attention. If the top and bottom ground planes are not at the same potential, a parallel-plate mode can propagate between them. If excited, this mode will not remain confined to the region near the strip but will be able to propagate wherever the two ground planes exist. It is more insensitive than microstrip to lateral ground planes of a metallic enclosure since the electromagnetic field is strongly contained near the center conductor and the top-bottom ground planes.