What is a Half Wave Rectifier?
A Half Wave Rectifier is defined as a type of rectifier that only allows one half-cycle of an AC voltage waveform to pass, blocking the other half-circle. Half-wave rectifiers are used to convert AC voltage to DC voltage, and only require a single diode to construct.
A rectifier is a device that converts AC to DC. It is done by using a diode or a group of diodes. Half wave rectifiers use one diode, while a full wave one uses multiple diodes. The working of this takes advantage of the fact that diodes only allow current to flow in one direction.
Theory
A half wave rectifier is the simplest form available. The diagram below illustrates the basic principle of it. When a standard AC waveform is passed through this kind rectifier, only half of the AC waveform remains. Half-wave rectifiers only allow one half-cycle (positive or negative half-cycle) of the AC voltage through and will block the other half-cycle on the DC side, as seen below.
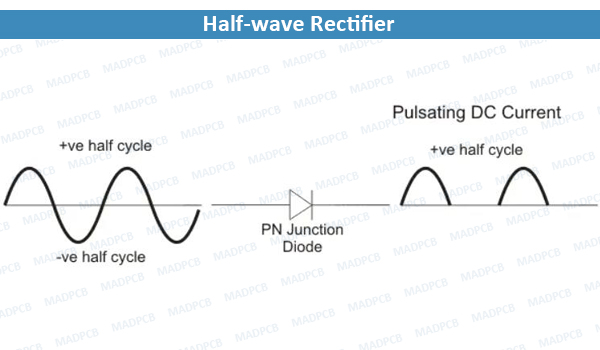
Half-wave Rectifier
Only one diode is required to construct a half-wave one. In essence, this is all that the half-wave rectifier is doing. Since DC systems are designed to have current flowing in single direction (and constant voltage – which we’ll describe later), putting an AC waveform with positive and negative cycles through a DC device can have destructive (and dangerous) consequences. So, we use them to convert the AC input power into DC output power.
But the diode is only part of it – a complete half-wave rectifier circuit consists of 3 main parts:
- A transformer
- A resistive load
- A diode
A circuit diagram looks like this:
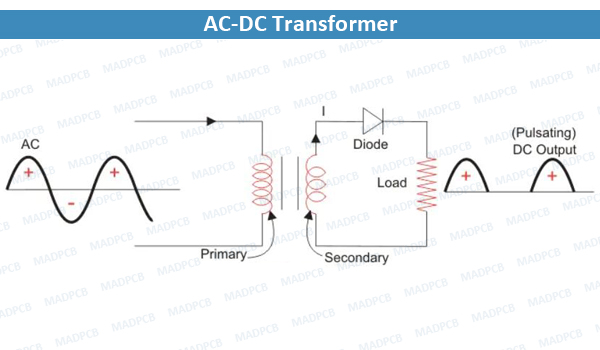
AC-DC Transformer
Advantages
- Half wave rectifier is a simple circuit.
- It has a low cost.
- We can ease to use it.
- We can easily construct.
- It has a low number of component, therefore it is cheap.
Disadvantages
- The transformer utilization factor is low.
- They produce a low output voltage.
- DC saturation of transformer core resulting in magnetizing current and also some hysteresis losses and generation of harmonics.
- The power output and therefore rectification efficiency are quite low. This is due to the fact that power is delivered only during the one-half cycle of the input alternating voltage.
- Ripple factor is high and elaborate filtering is, therefore required to give steady dc output.
- They only allow a half cycle through per sinewave, and the other half cycle is wasted. This leads to power loss.
