What’s Peak Inverse Voltage?
Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV) is the maximum rated value of an AC voltage acting in the direction opposite to that in which a device is designed to pass current.
In semiconductor diodes, PRV (peak reverse voltage) or PIV is the maximum voltage that a PN junction, or a diode can withstand in the reverse direction without breaking down or avalanching. However, if the voltage coming across the junction at reverse biased condition increases beyond this specified value, the junction will get damaged. Diodes must have a PIV rating that is higher than the maximum voltage that will be applied to them in a given application.
For rectifier applications, PIV or PRV is the maximum value of reverse voltage which occurs at the peak of the input cycle when the diode is reverse-biased. The portion of the sinusoidal waveform which repeats or duplicates itself is known as the cycle. The part of the cycle above the horizontal axis is called the positive half-cycle, or alternation; the part of the cycle below the horizontal axis is called the negative alternation. With reference to the amplitude of the cycle, the PIV is specified as the maximum negative value of the sine-wave within a cycle’s negative alternation.
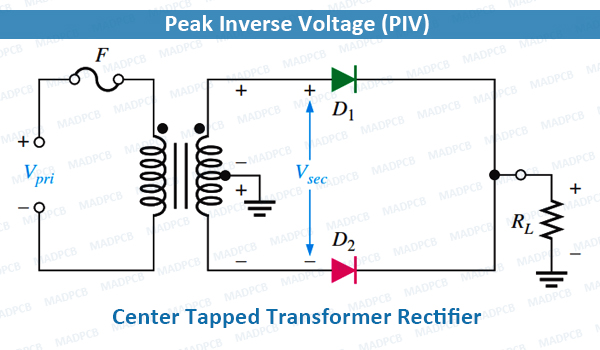
Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV)
