What’s Wavelength?
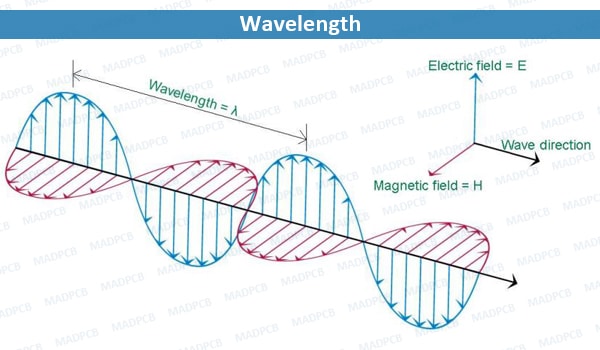
In physical, the Wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave – the distance over which the wave’s shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek Letter lambda (λ).
The term wavelength is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. In printed circuit board design and manufacturing, we need to keep attention to impedance controlled and high frequency boards.
Frequency vs Wavelength
In the case of traveling waves, the frequency of a wave is correlated to the wavelength of the wave and the speed at which the wave is traveling. If a wave is moving faster, the number of complete wave cycles that will complete in 1 second is higher than when compared to a slower wave. So, the speed at which a wave is moving is a very important factor when determining its frequency.
Transmission Line
A transmission line is an interconnect used to guide electromagnetic wave or electrical energy from one point to another with the intention of least possible loss and distortion. Transmission lines are extensively used by RF engineers in the design of RF circuits and RF PCBs. For example, to transfer the RF energy from transmitter to antenna, RF engineers use transmission line in place of normal electric wire or normal PCB trace. A normal PCB trace or electric wire creates too high a loss and distortion to the electric energy. If a transmission line is used instead, it will transfer the energy from the transmitter to the antenna with almost zero loss of energy. In high speed digital transmission, the use of transmission lines lead to less distortion and lower loss.
The characteristics of the transmission line depend upon the physical dimensions. A transmission line can be formed using PCB traces, coaxial cables, wave guides, twisted pair, shielded pair etc. As PCB designers we will see how transmission lines can be formed using PCB traces. The same electric wire on the PCB traces which we call ordinary point to point wiring can become transmission line if we follow certain basic rules e.g., define the ratio of the PCB trace width and its separation from ground plane.
A microstrip is a transmission line used for signals in the microwave range. It was invented because of the undesirable effects on coaxial cable when signals in the microwave range propagate through it. The wavelength of the signal that can propagate effectively inside a microstrip is called the guided wavelength.